Entire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
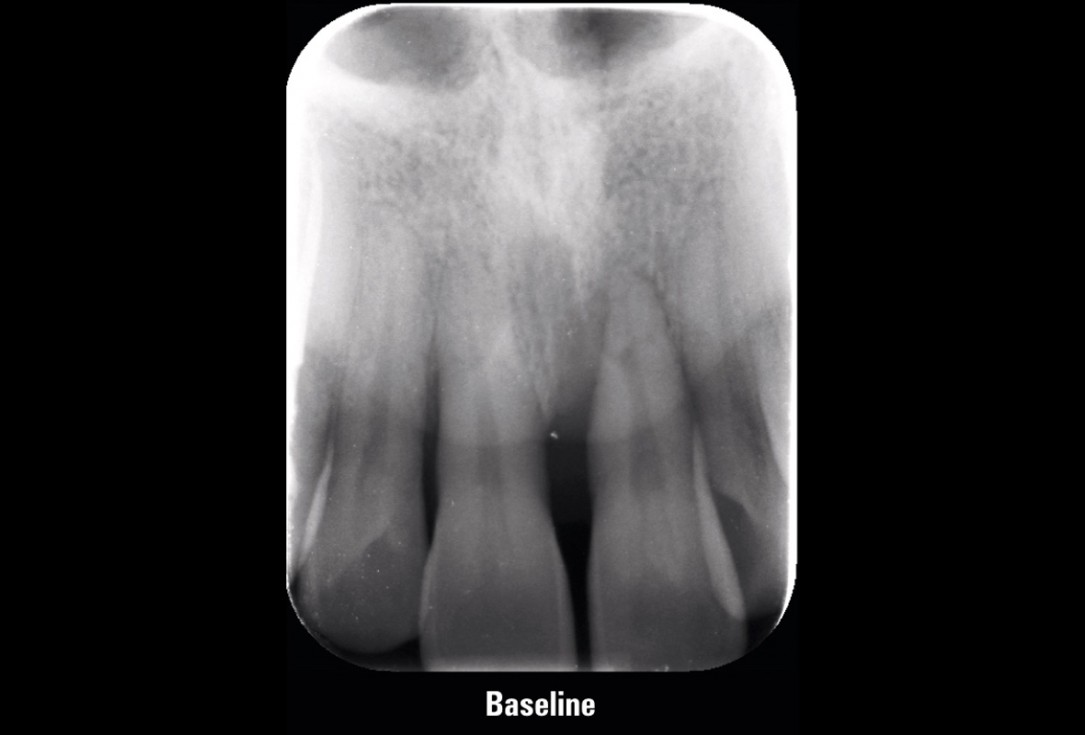
01/11 - Initial X-ray presenting a very deep intrabony defect of tooth 21Entire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
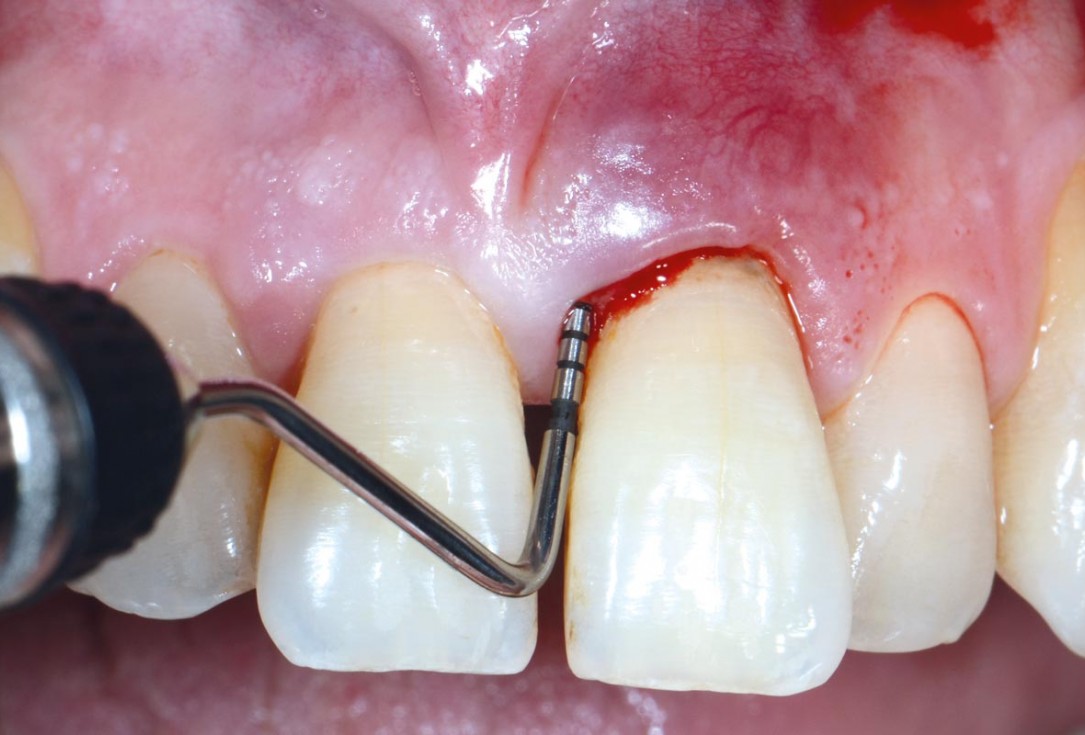
02/11 - Initial probing depth of 12 mm before non-surgical therapyEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
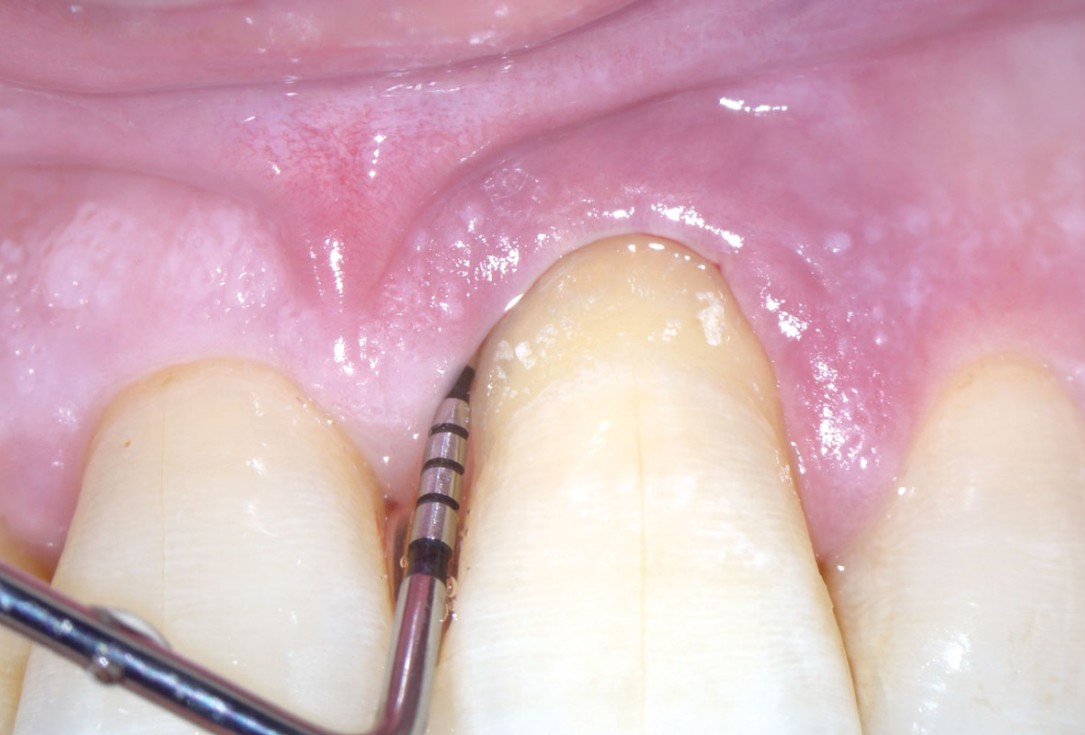
03/11 - Probing depth of 10 mm after non-surgical therapy with a 13 mm clinical attachment level (CAL)Entire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
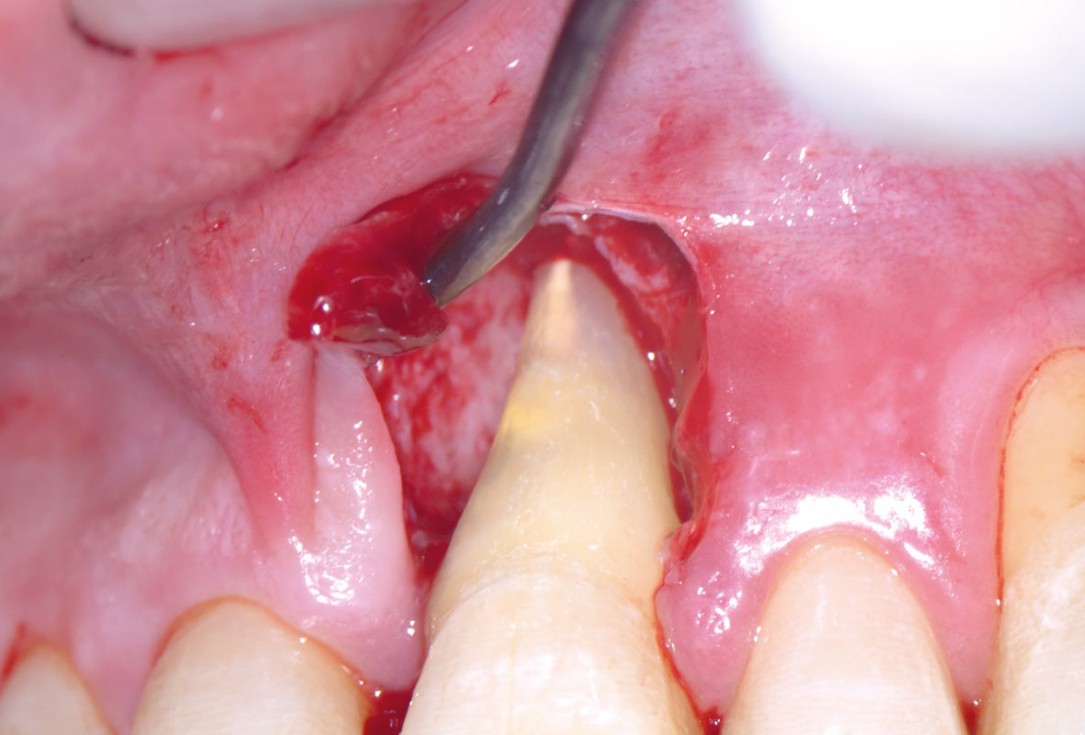
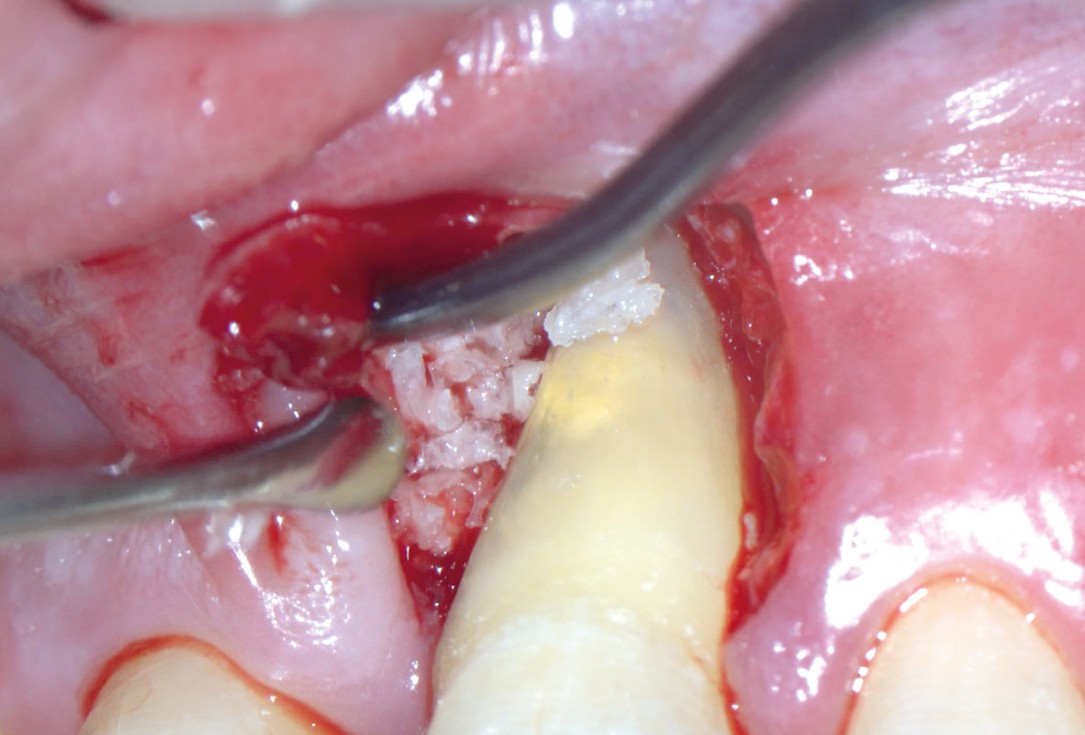
04/11 - Access to the defect using EPP technique by avoiding an incision over the defect-associated papilla. Note: the osseous defect involving the apexEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
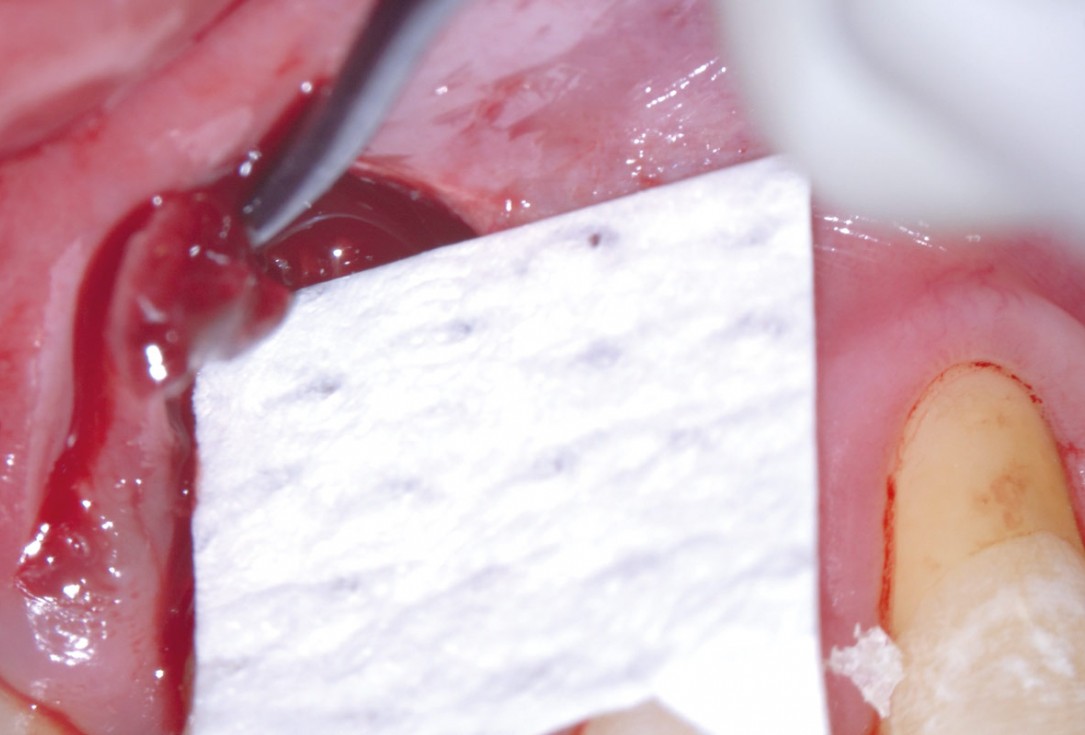
05/11 - Application of maxgraft® granules to fill the defectEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
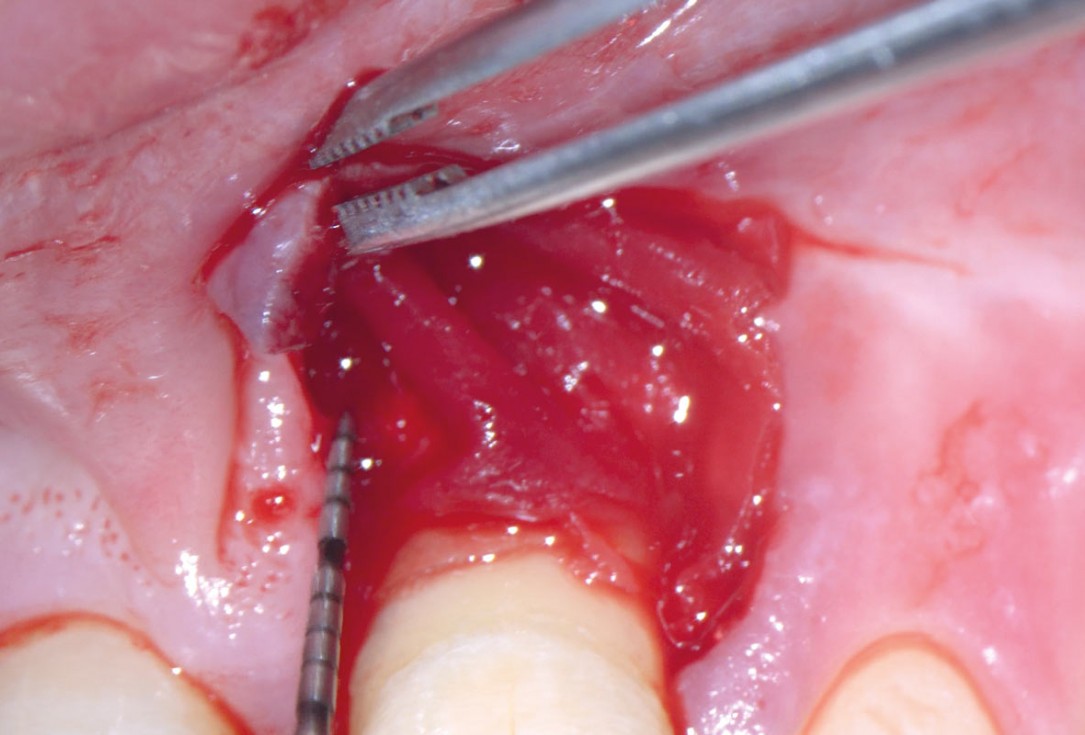
06/11 - Trimming of collprotect® membrane according to the osseous defect morphologyEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
07/11 - Application of the membrane to cover the defect, stabilised with suturesEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
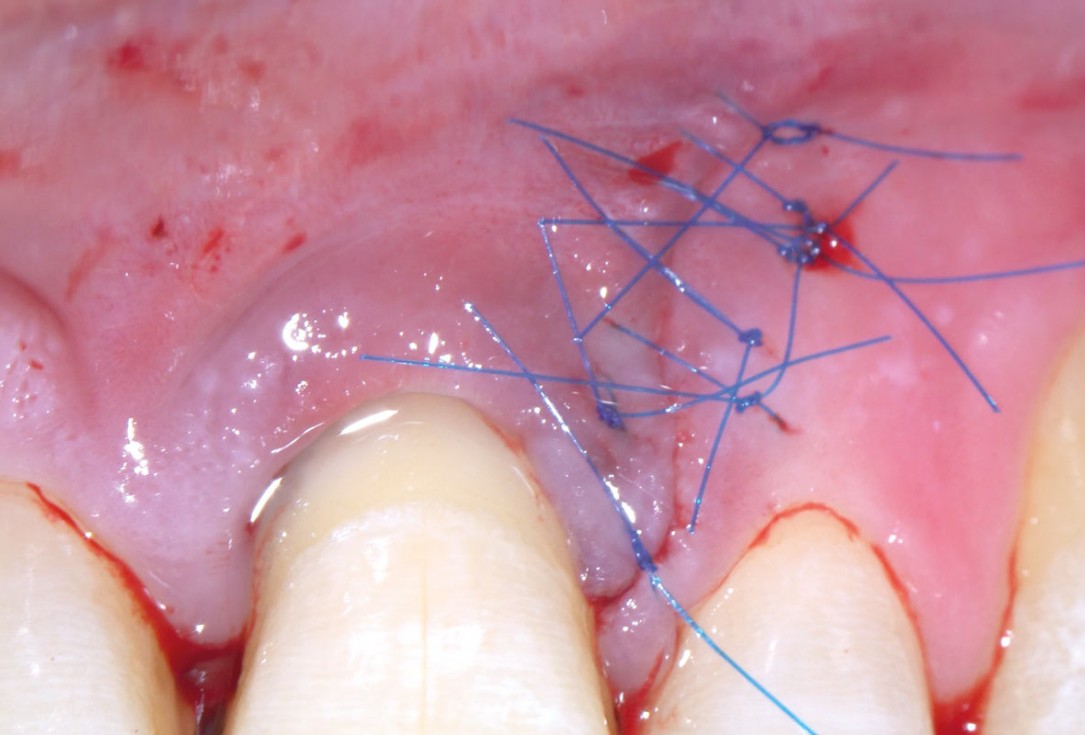
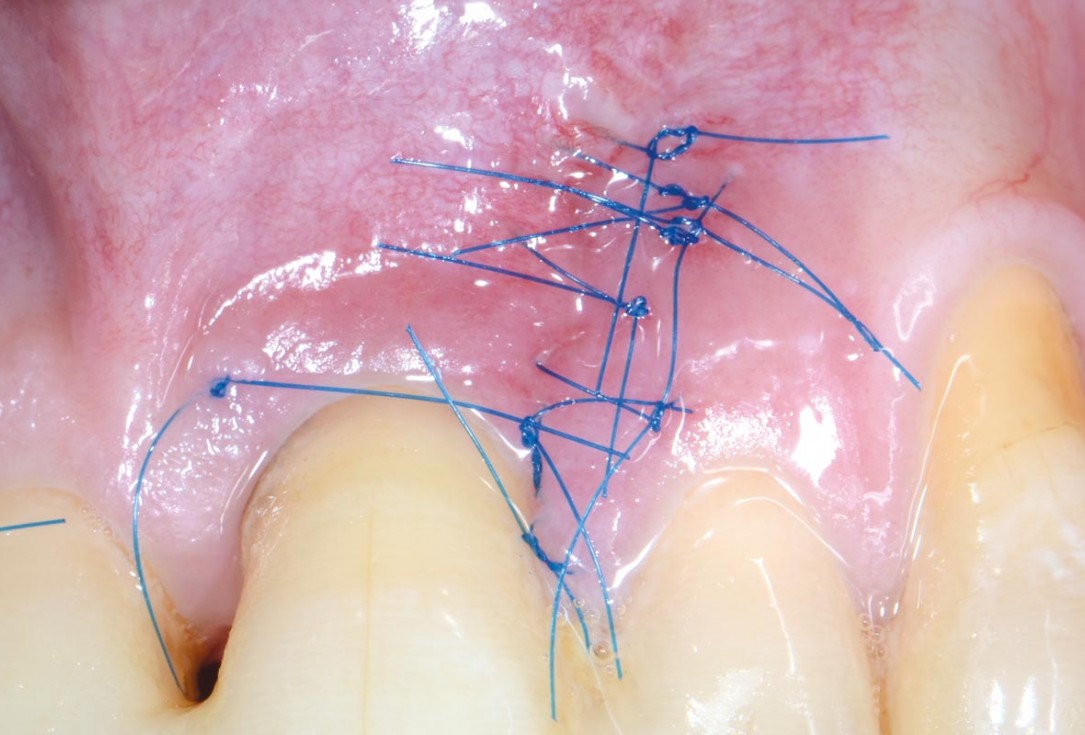
08/11 - Primary wound closure with microsurgical suturing techniqueEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
09/11 - Early wound healing at 7 days post-operativeEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
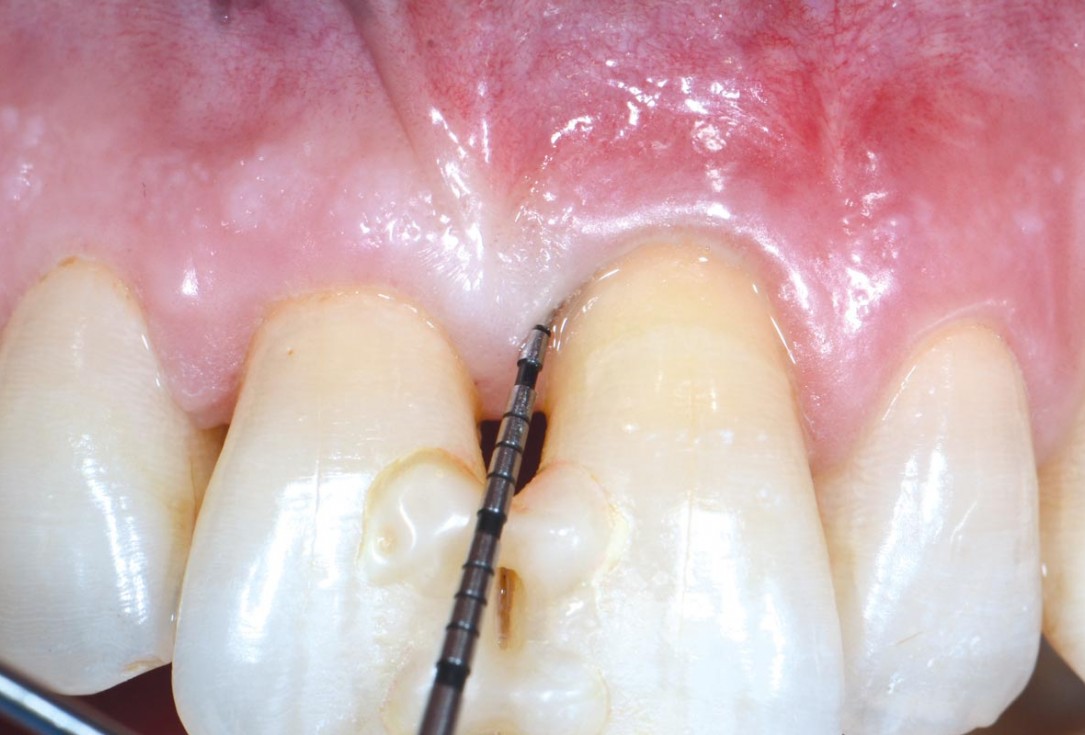
10/11 - Resolution of the defect at 1-year with 3 mm probing depth and 7 mm CAL gainEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
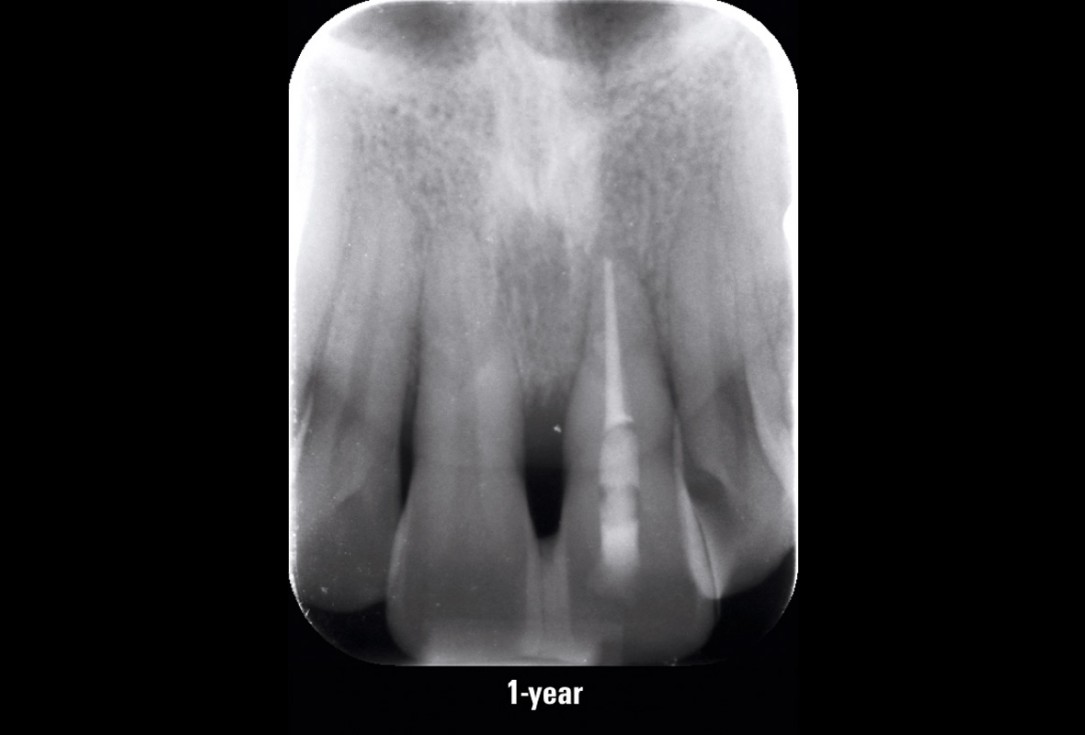
11/11 - Control x-ray at 1-year follow-upEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan

Baseline clinical situation.

Situation before extraction of the teeth

Initial clinical situation

Initial situation after extraction of tooth 21 after 6 months

Preparation of a single tooth defect with severely resorbed vestibular wall

Initial clinical situation.

Initial clinical situation

Tooth 16 furcation involvement with gingival marginal recession and large Class 5 filling

Initial x-ray, ten years post implantationem alio loco, large peri-implant bone loss

Extraction socket with bone wall defect

Situation before tooth extraction

Initial clinical situation

Initial X-ray presenting a very deep intrabony defect of tooth 21

Implant placed in the deficient site. permamem® in place for covering.

Initial situation – Treatment plan: Replace the adhesive upper left central incisor bridge with a dental implant

Occlusal view of attached maxgraft® cortico at the buccal site

Initial x-ray, tooth 25 compromised and to be extracted

Clinical situation at baseline: Situation after tooth extraction UR1 due to a failed endodontic treatment 3 months previously

Alveolar socket before soft and hard tissue augmentation

Pre-operative situation; tooth 21 proved not to be worth preserving

Initial clinical situation: 9 mm pocket depth associated with root fracture

Initial situation - A young female 34 years old lost her front teeth in an surfing accident and she had a 5 unit bridge supported by her upper left lateral and right canine. The restoration failed and both supporting crowns have exposed and leaking margins.

Initial situation - endodontically failing tooth 22, very thin biotype, high lip line and esthetic expectations

Preoperative x-ray, severe bone atrophy

Initial situation - broken and missing upper right central incisor (UR1). This tooth was removed long time ago and there were signs of bone loss and resorption due to the bone remodelling. Patient was also undergoing orthodontic treatment due to the loss of mesio-distal space.