Entire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
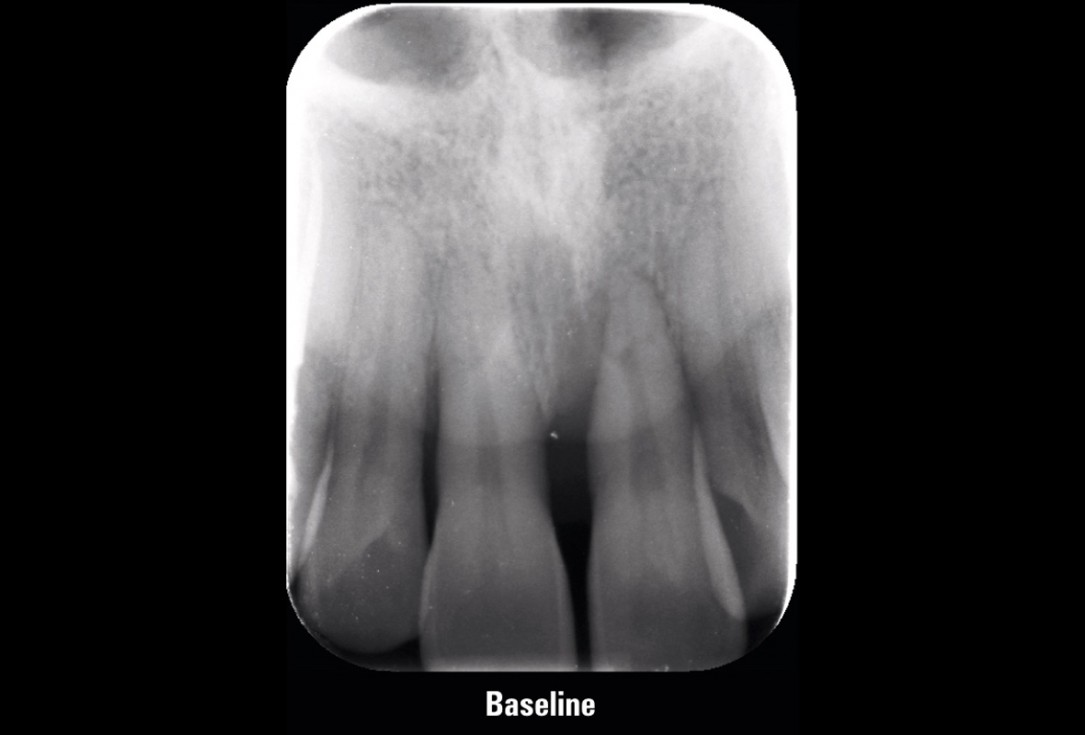
01/11 - Initial X-ray presenting a very deep intrabony defect of tooth 21Entire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
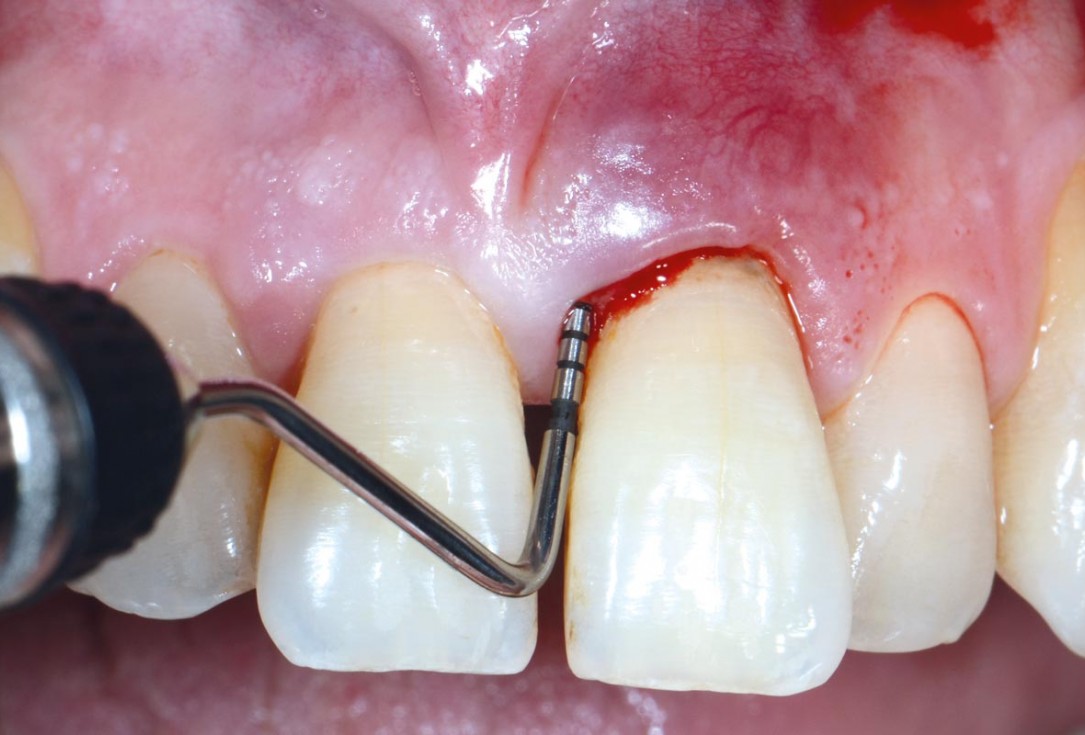
02/11 - Initial probing depth of 12 mm before non-surgical therapyEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
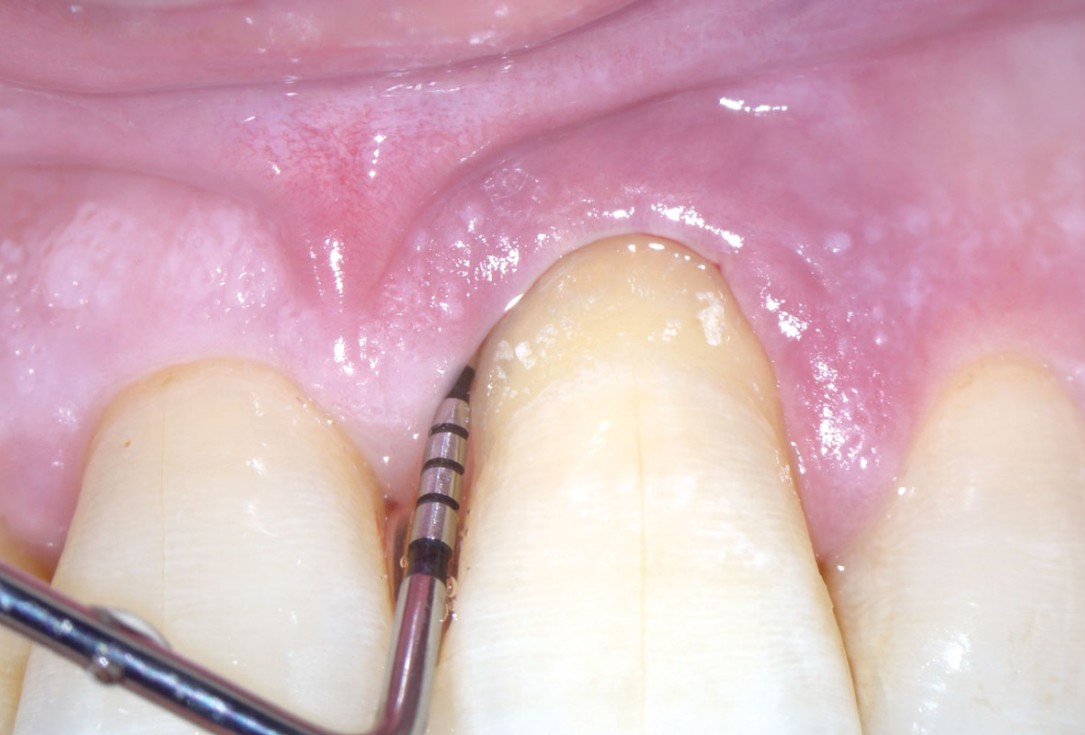
03/11 - Probing depth of 10 mm after non-surgical therapy with a 13 mm clinical attachment level (CAL)Entire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
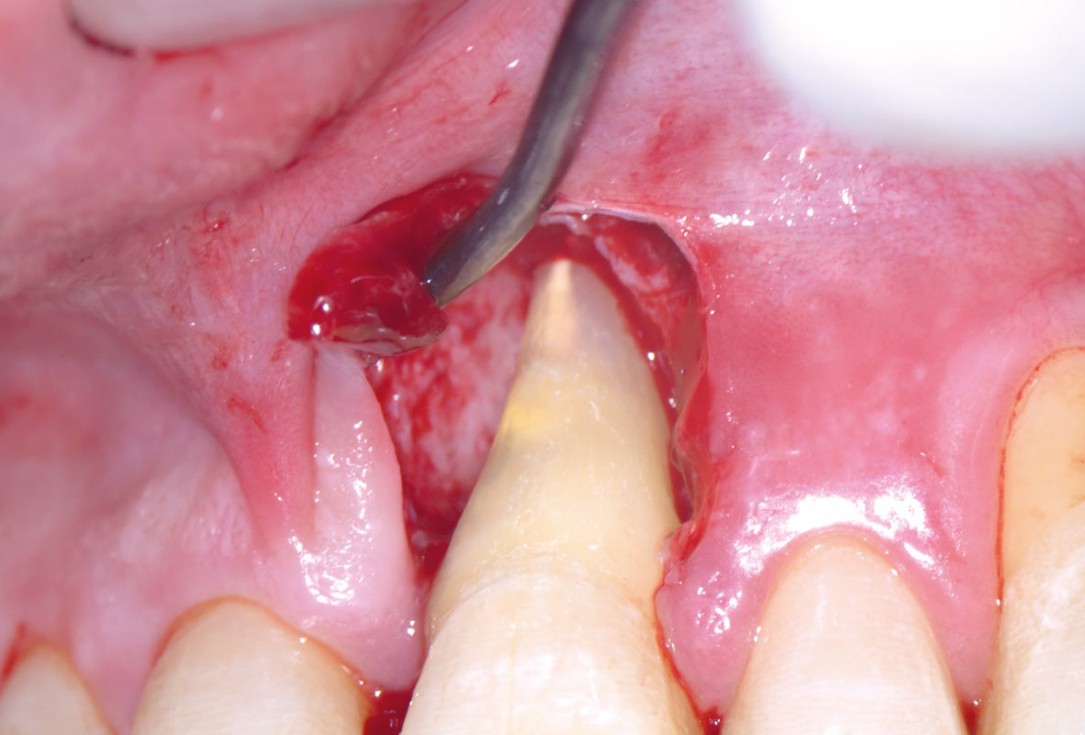
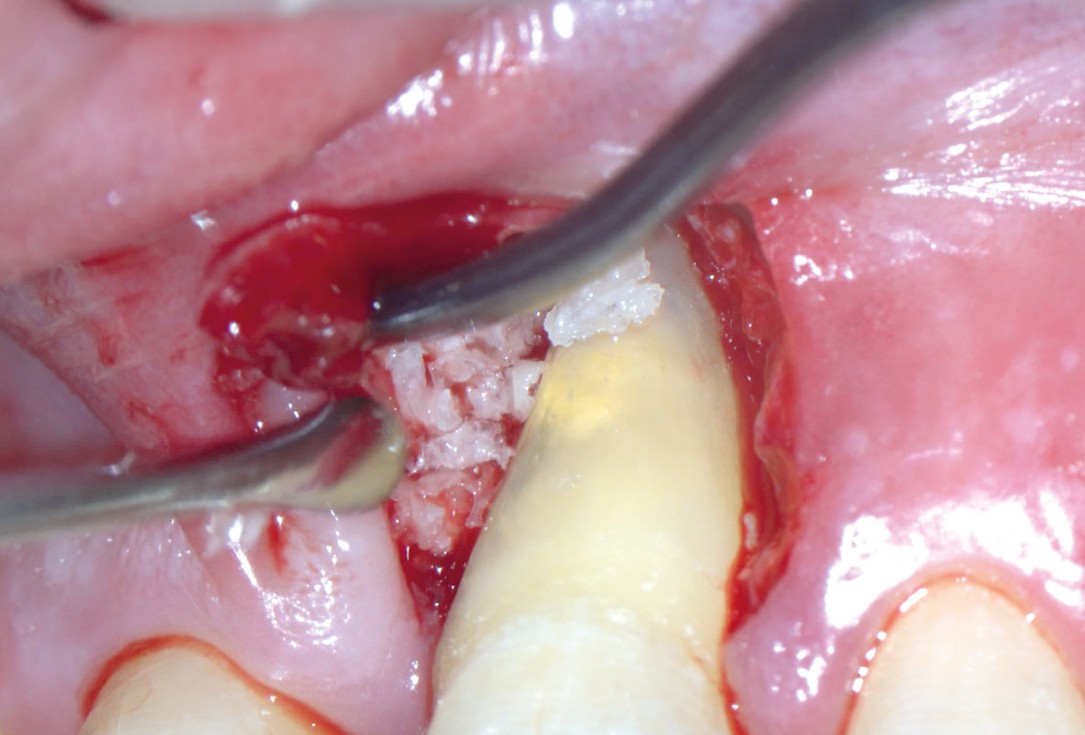
04/11 - Access to the defect using EPP technique by avoiding an incision over the defect-associated papilla. Note: the osseous defect involving the apexEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
05/11 - Application of maxgraft® granules to fill the defectEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
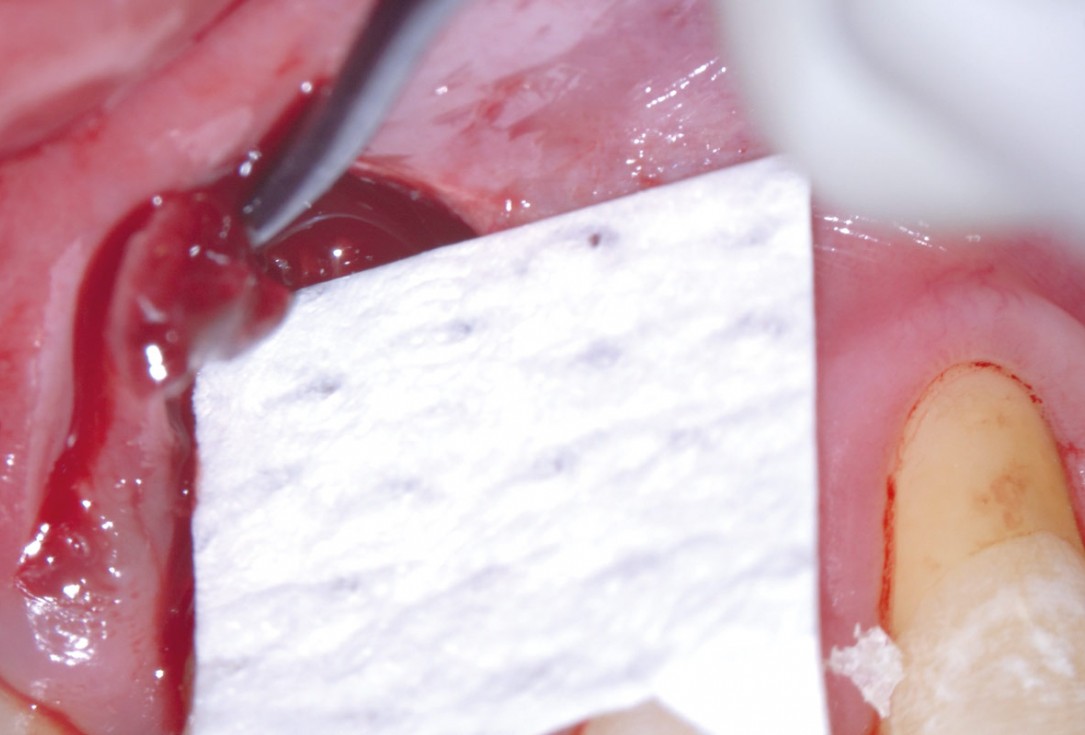
06/11 - Trimming of collprotect® membrane according to the osseous defect morphologyEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
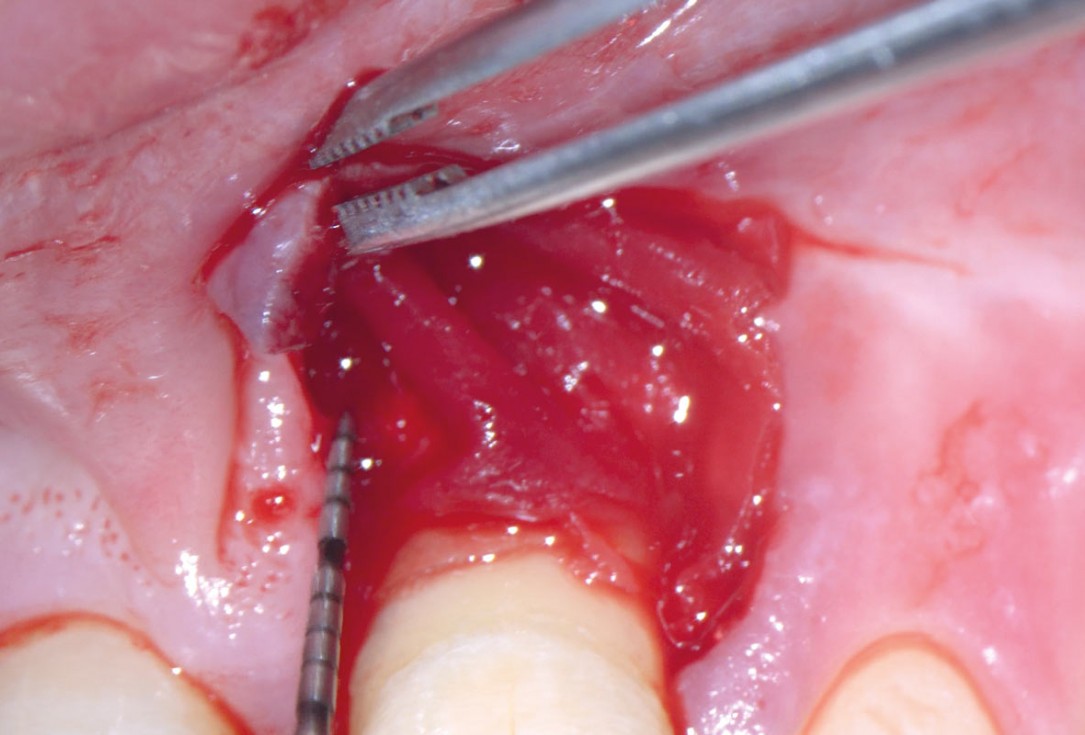
07/11 - Application of the membrane to cover the defect, stabilised with suturesEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
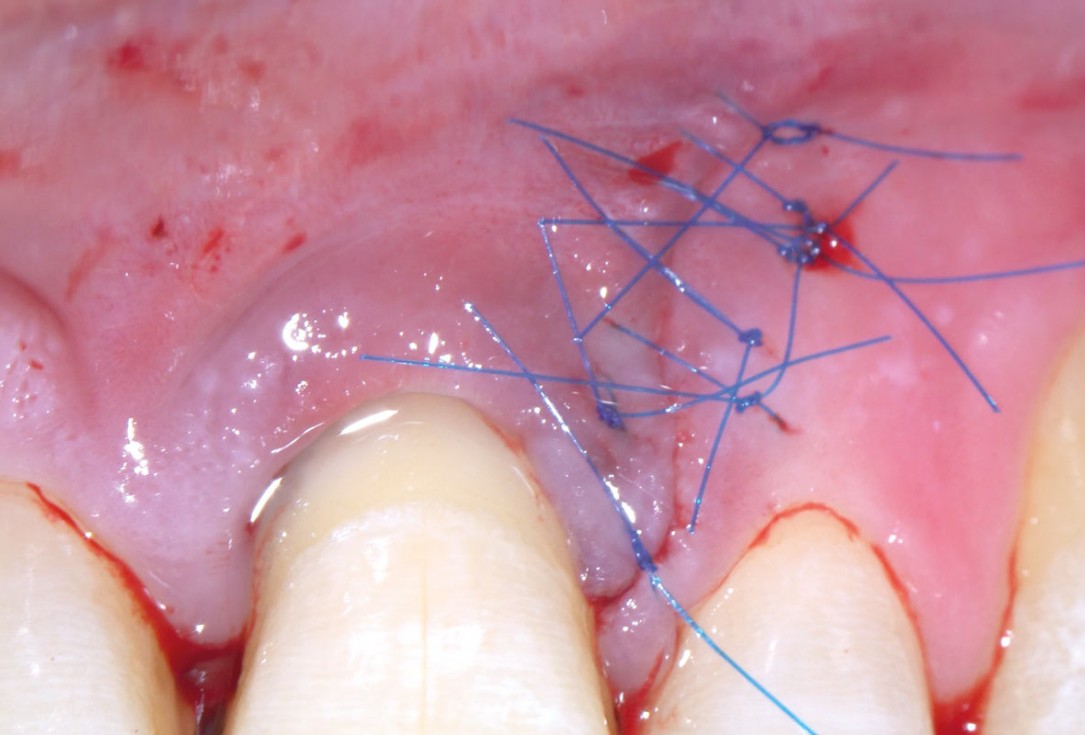
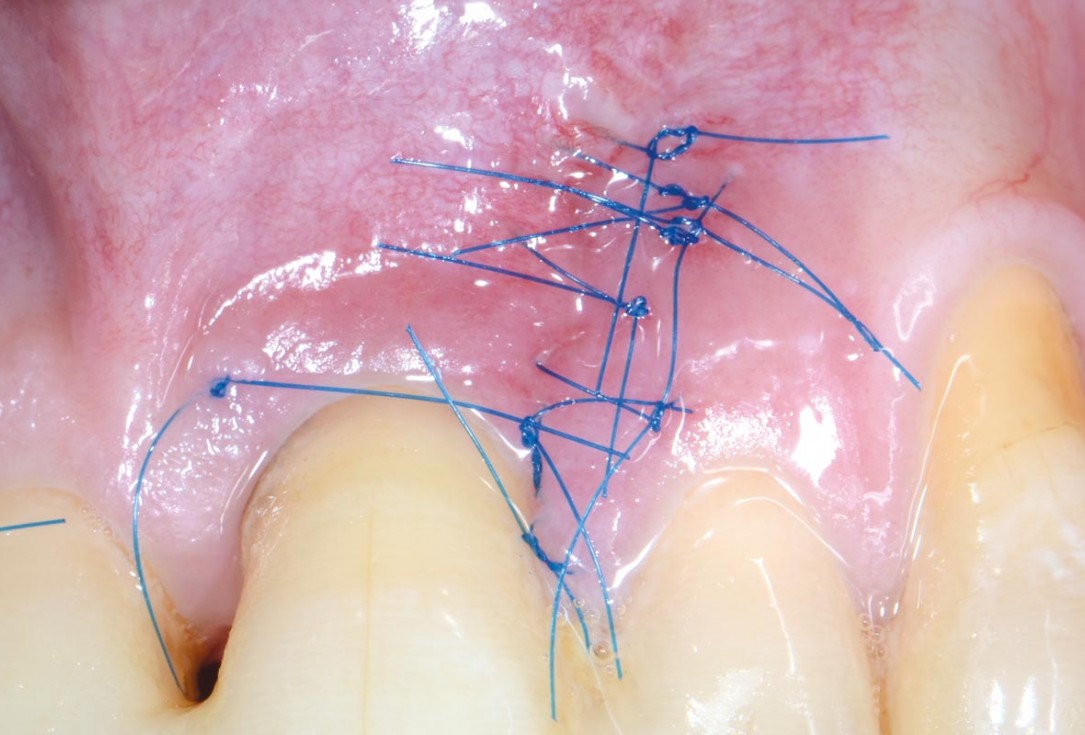
08/11 - Primary wound closure with microsurgical suturing techniqueEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
09/11 - Early wound healing at 7 days post-operativeEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
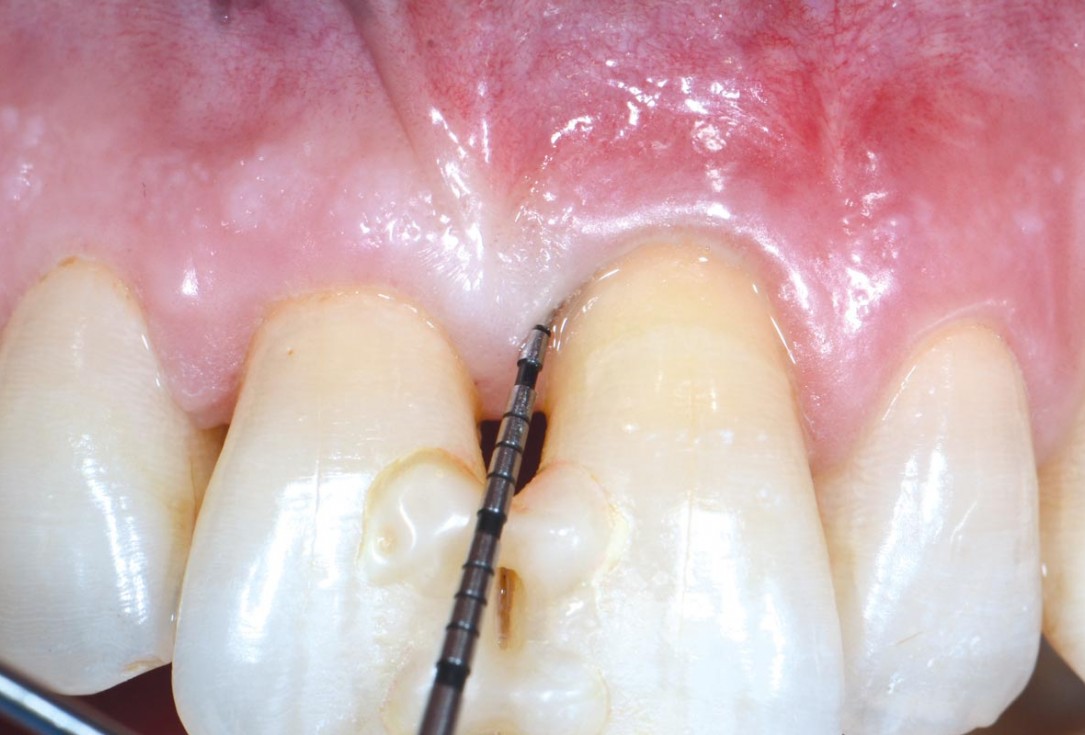
10/11 - Resolution of the defect at 1-year with 3 mm probing depth and 7 mm CAL gainEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan
-
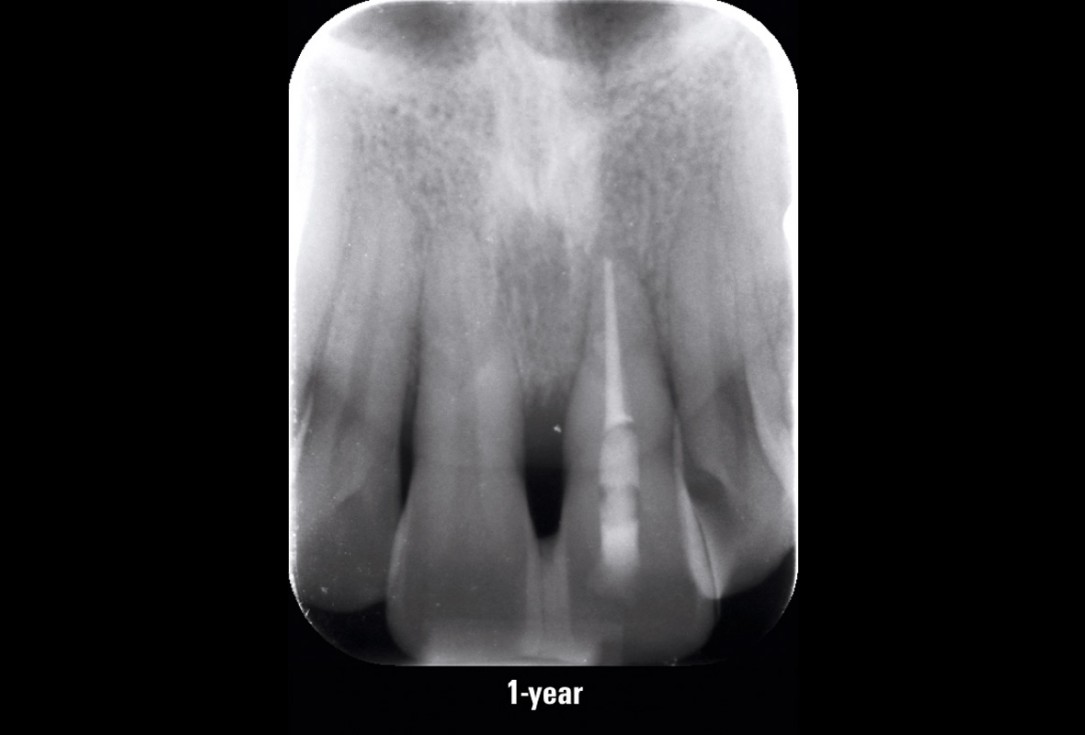
11/11 - Control x-ray at 1-year follow-upEntire papilla preservation technique (EPP) for the regenerative treatment of a severely compromised central incisor - Dr. S. Aslan

Pre-operative OPG shows deep vertical intrabony defects on the distal aspects of teeth 13 and 14.

Pre-surgical probing reveals a deep intrabony defect on the distal aspect of the upper canine.

Pre-operative radiograph. Intrabony defect on the mesial aspect of tooth 14.

Surgical presentation of the alveolar ridge with reduced amount of horizontal bone available

OPG of the initial situation – provision of missing denture in regio 44 to 47 by a resin-retained bridge

Baseline clinical situation.

Situation before extraction of the teeth

Initial clinical situation

Initial situation after extraction of tooth 21 after 6 months

Preparation of a single tooth defect with severely resorbed vestibular wall

Surgical presentation of the alveolar ridge with reduced amount of horizontal bone available

DVT control after sinusitis surgery, residual bone height 1 mm

DVT image showing the reduced amount of bone available in the area of the mental foramen

Extraction socket with bone wall defect

Situation before tooth extraction

Initial clinical situation

Clinical situation with narrow alveolar ridge in the lower jaw

Extended horizontal and vertical defect of the maxilla following tumor resection and reconstruction with a scapula graft

Clinical situation of the edentulous distal maxilla before the surgery

Pre-operative x-ray control

The patient presented with a terminal fracture of the crown tooth number 12

Alveolar socket before soft and hard tissue augmentation

Pre-operative situation; tooth 21 proved not to be worth preserving